Difference Between SQL JOINs and UNION
Mastering JOINs and UNIONs is essential in becoming an expert in database communication.
Here’s what we’ll cover in this article:
- Introduction
- What a join is
- How Joins work
- Types and examples of Joins
- What Union is
- How Union works
- Types and examples of Union
- Differences between the two
This write up explores the differences between Join and Union in a RDBMS.It also highlights the specific use cases for each clause, equipping individuals (tech bros/sis) who are new to SQL with a clear understanding of when to use either of the two when querying a database.
What are JOINs?
A SQL Join is a command clause used to combine rows of a dataset from two tables based on a related column.
This basically means that when using Joins the tables involved must have a similar column.
Syntax
SELECT column_name FROM table1 JOIN table2 ON table1.similar_column=table2.similar_column;
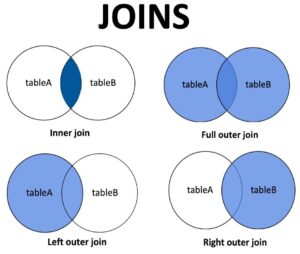
Types of Joins:
- (INNER) JOIN: Returns records that have matching values in both tables.
- LEFT (OUTTER) JOIN: Returns all records from the left table and the matching records from the right table.
- RIGHT (OUTER) JOIN: Returns all records from the right table and matching records from the left table.
- FULL (OUTER) JOIN: Returns all records when there is a match in either left or right table
What are SQL UNIONs?
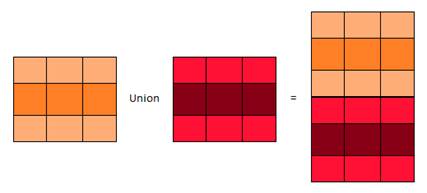
Union is a SQL clause used to combine the result set of multiple Select statements into a distinct single result that includes all the rows that belongs to all the queries in the Union.
There are a few rules to follow when using Union:
- Every Select statement within union must have the same number of columns
- The columns to be combined must also have similar data types
- The columns in the two Select statement must also be in the same order
Syntax
SELECT column_name FROM table1 UNION SELECT column_name FROM table2;
What are the major differences between the two?
| JOIN | UNION | |
| 1. | It combines the records into new columns | It combines the records into new rows |
| 2. | Columns in the two tables may not be equal and not in the same order | Columns in the two table must be equal and in the same order |
| 3. | The data types of the columns do not have to be similar | The data types of the columns in the two SELECT statement must be the same |
| 4. | The JOIN clause duplicates rows in the result set | The UNION clause does not replicate rows in the result set |
Check out the following Examples:
UNION
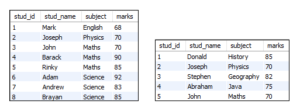
We have a table here called ‘Student1’ and ‘Student2’ in our sample database.
This website doesn’t have an online compiler so we just assume these are the contents of the table below:
We type the following statement:
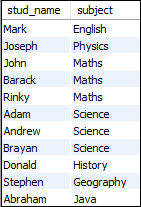
SELECT stud_name, subject FROM student1 UNION SELECT stud_name, subject FROM student2
The SQL statement above selects the students name and subject from the two tables (using the Select command) and combines them together.
Result set below:
Note:The number and order of the columns in the two tables are the same.
JOINs
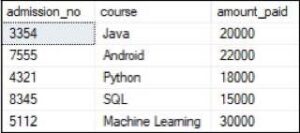
Suppose our database has the following tables: ‘Student’ and ‘Fee’ that contains the data below:
Table-Student
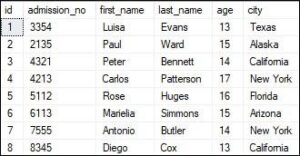
Table-Fee
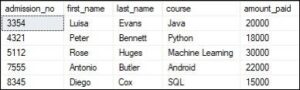
We can demonstrate Inner Join using the following statement:
SELECT Student.admission_no, Student.first_name, Student.last_name, fee.course, fee.amount_paid FROM Students INNER JOIN Fee ON Student.admission_no =Fee.admission_no;
We’ll get the following result set:
In conclusion, SQL Joins and Union serve different purpose and are used in different situation when querying a database
- JOINs are about connecting tables and retrieving related data.
- UNION is about combining results from different SELECT statement into a unified result set.